AP宏观经济备考经验,你值得拥有!
2019-11-19
对于要考AP宏观经济的小伙伴来说,考试经验是不是很诱人呢?今天,小学诚咨询了几位学长,为大家总结了AP宏观经济备考心得,一起来看看。
A. Basic Concept.
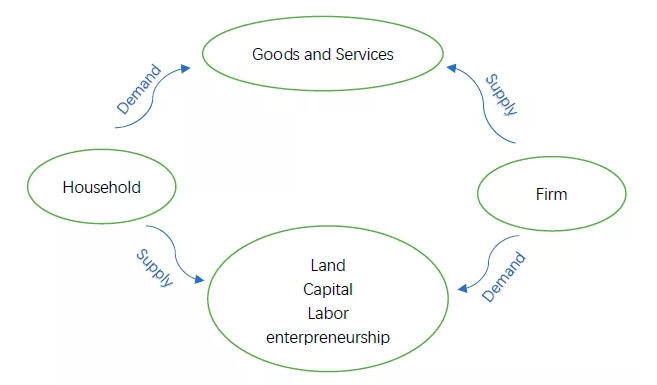
1.Relationship between household and film
2.General Domestic Product(GDP)
几点需要注意:
1: It represent the final market value.
2: All services and goods in the market.
3: in only one country.
4: in a period of time (a year)
不能算作GDP的情况,如:1900年的古董今年再售卖,只能算1900年的GDP不能算是2018年的。(因为古董是在1900年生产的)
3. Nominal GDP=current price * current quantity
Real GDP=base year price * current quantity
4. Price index (价格指数)
Consumer price index (消费者价格指数): measureschanges in the price level of a market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households.
(Overestimate the true burden of inflation because it does not recognize consumers’ ability to substitute goods and services as price change. (选择题考过))
Producer price index(生产者价格指数):the average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output.
5. GDP deflator=(Nominal GDP/Real GDP)*100
RGDP>NGDP : Deflation
RGDP<NGDP : Inflation
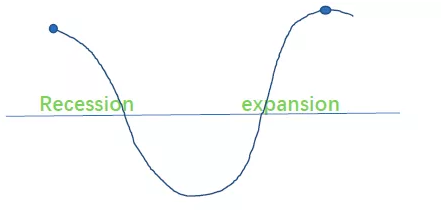
6.Business Cycle(选择题考过)
7. Main Reasons for economic growth(常考,几乎选择题必考):
1. More resources
2. Higher level of education
3. Increase technology / productivity
Methods to improve Human Capital:
Education/Training
Better skills
8. Disposable income=personal income-tax
9. Consumption=autonomous consumption + derived consumption
autonomous consumption: consumption expenditure that occurs when income levels are zero.
derived consumption:Consumption for a factor of production or intermediate good occurs as a result of the consumption for another intermediate or final good.
10.Nominal interest rate-Inflation=Real interest rate(常考)
B. Three main theory
1. Monetarist(很少考):increasing the money supply at a rate equal to the GDP increase rate.
2. Classical(比较常考,答题也有出,关键词:Government take no actions): emphasize economy is fairly stable(强调市场内在稳定),can cure the recession; and no government intervention(没有政府介入); Flexible market.
3. Keynesians(常考):emphasize that economy is unstable. (Sticky market);Recommand active government policy.(fiscal policy is more effective than monetary policy);Liquidity trap
Example for classical theory:
When economy is in Recession ,there is surplus of workers or inputs ,the wage and the cost will decrease
AS curve will shift to right for get equilibrium level.(没有政府介入,市场自动恢复)
C.Crowding out and Stagflation(常考)
Crowding out effect :通常指政府的开支增加导致的私人投资和消费减少。
通常思路是:GS(government spending)increase Demand for loanable fund increase real interest rate increase people tend to save money in the banks rather than use it to invest, so that investment and consumption decrease, AD shift to left.反之亦然。
Stagflation:跟理性预期很像。
逻辑是:When AD curve shift to right ,price level increase。people are expecting for a higher price level。 so that producers tend to save products rather than sell it since they are waiting for a higher price level which can make more profit for them.
D. Unemployment(选择题必考)
1. 计算方法:失业人口/总劳动力
失业人口指:
1.People have ability to work but do not have job.
2.People who is finding new job.不是失业人口的情况:Tony在一个志愿者中心无薪工作,期间拒绝一切工作的offer,这种情况Tony不能算是劳动力。
2. FOUR kinds of unemployment;
1. Frictional unemployment:摩擦性失业,A person switch to a new job.可以理解为跳槽期间的空档时间。
2. Structural unemployment:结构性失业, A kind of skill is being replaced by machines, therefore there is no requirement for this kind of skill-worker anymore.(技术不再被市场需求)
3. Cyclical unemployment:周期性事业, A person was being unemployed since the economic change, such as recession or depression.
4. Seasonal unemployment:季节性失业,A person was unemployed since the seasonal change.
3. Dishonest workers: 不是失业人口却拿补助金的人。会导致unemployment rate 上升。
4. Natural unemployment rate:around 5%, only in structural unemployment and frictional unemployment.
5. Discourage workers: People who do not want to find job, and will not account in labor force.
E. Multiplier
1. MPC:Marginal propensity to consume(边际消费倾向)
MPS:Marginal propensity to save
MPC=change in consumption/change in income
MPS+MPC=1
2. Government spending multiplier: GS*(1/1-MPC) OR GS*(1/MPS)
3. Balanced Budget: (1/1-MPC)*(-MPC/1-MPC)=1(常考考点:政府开支和税同时增加相同的量,他们的乘数效应一样吗?答案是!不一样,因为政府开支的乘数比税的乘数大。)
F. Monetary Policy
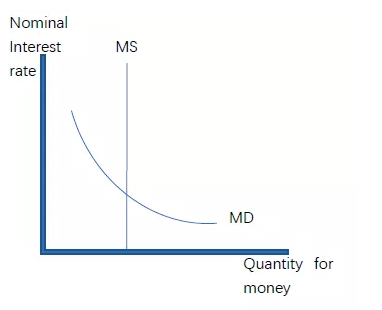
1.最最最常考,必须记住的:导致Money Supply增加的三个原因:
Required reserve rate decrease
discount rate decrease
Central bank buy goverment bonds (这个相比前面对nominal interest rate影响最小)
反过来,导致MS 减少的三个原因:
Required reserve rate increase
Discount rate increase
Central bank sell goverment bonds
2.Federal funds rate: the interest rate of loan between commercial banks.
3. Discount rate: the interest rate that a country’s central bank charges to other banks.
4.股票价格=股息/利率
5.National debt: the accumulation of past and current budget deficits and surplus.
6. current account/financial account
Current account: services/goods/products/transfer
Financial account: shock/directly investment (factory) and indirectly investment/bonds
(如果其中一个deficit,另外一个就surplus)
7.Tax credit:税收减免 (Real tax decrease, led to an increase in investment)
G.Phillips Curve
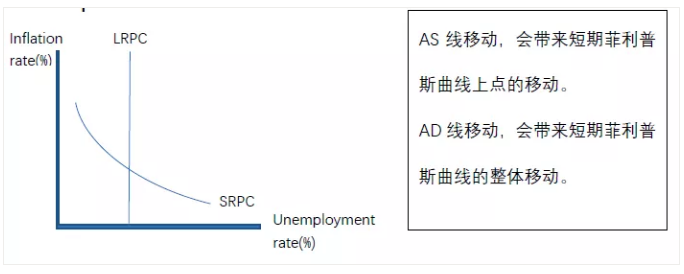
H. Exchange Market
重点:
1.对一个国家货币需求上升,同时另一个国家的货币供给也会上升。
2.Interest rate increase Appreciation Export decrease and import increase
3.Interest rate decrease depreciation Import decrease and Export increase
4.Import traffic increase Import decrease Demand for foreign currency decrease and Supply for domestic currency decrease
这就是小学诚为大家整理的满满知识点,希望对同学们有帮助哦~AP考试有疑问的小伙伴,试听课走起!



